
Muscle spasticity is a clinical sign of numerous neurological disorders, such as ischaemic strokes, multiple sclerosis, hypoxic cerebral damage, traumatic brain damage, spinal injuries, tumors and degenerative diseases.
According to the WHO, spasticity refers to tense and rigid muscles or unusual muscular tension as well very strong or exaggerated tension, as for instance a knee-jerk reflex.
What is muscular spasticity?
Spasticity is a phenomenon of liberation causing a loss of inhibiting mechanisms after an injury of the upper motor neurone that allows reflex muscle activity or due to an excessive and uncontrolled muscle tone associated with involuntary movements, clonus and increased muscle tone.
After a brain injury or cerebral palsy, muscle spasticity causes various medical complications, function deterioration and loss of quality of life. This is very common in cases of ischaemic strokes, which make up 20% to 40% of all cases, where a gradual development of spasticity is seen in the course of the first months after the stroke.
It also very common in patients with spinal cord injuries (SCI), caused by an accident or trauma. It can cause paralysis from the waist down (paraplegia) or from the waist up (tetraplegia). 80% of all patients with spinal cord injuries experience pain, requiring an adequate treatment.

Many studies with different protocols have been carried out with the aim to determine the anti-spastic effect of peripheral magnetic stimulation (Kanjanapanang y Col 2020). In some of these studies, peripheral magnetic stimulation was applied on the spinal nerve roots, while in other studies, the stimulation was applied to the spastic muscles.
All the studies showed consistent results: spasticity was reduced after each session of peripheral magnetic stimulation. Nevertheless, in order to understand how peripheral magnetic stimulation can reduce muscle spasticity, more investigation is needed (Beaulieu, Schneider 2013, Krewer y Col 2014).
Application of electromedical therapies and their benefits for muscle spasticity.
In order to control muscle spasticity after a SCI, several management methods have been applied. Ranging from medicine to stretching exercises, cryotherapy, nerve blocking by means of alcohol or phenol, electric stimulation or antispastic braces.
In case of uncontrolled spasticity, neurosurgical options can be considered, such as selective dorsal rhizotomy, continuous infusions of intrathecal baclofen, myotomy or tenotomy. Nevertheless, these surgical procedures are invasive and remain often unsuccessful, which is why they are really considered as a treatment option in case of spasticity.
On the other hand, electrical therapy has been used for functional electrical stimulation and as a complement of physiotherapy. It can be beneficial for certain individuals suffering from pathologies affecting the upper motor neurons that cause foot drop (Burridge y Col 1997). In these cases, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation was applied and it was discovered that it reduces muscle spasticity through its nociceptive and pain reducing action.
Heat has also been used to increase muscle elasticity, causing the spastic muscles to relax. The used techniques include ultrasound, fluid therapy, paraffin and superficial warmth. These techniques need to be combined with stretching and exercise (Lehmann, de Lateur 1982).

High intensity electromagnetic fields move to the neuromuscular tissue and induce electrical currents, depolarizing the neurons that produce the concentric muscular contractions.
The antispastic effect is achieved through post-facilitation induction that affects control of muscle tone at the spinal level. (Fisiopedia Http, Véle 1997).
Also, in more recent investigations (Krewer C, 2014), it was shown that the application of a high intensity electromagnetic field generates major blood perfusion in the exposed area, which leads to improved circulation and trophic improvement, relaxing the spastic muscles and stimulating the weakened muscles with the goal of obtaining a muscle balance and reducing spasticity in the affected area.
The influence of magnetic stimulation of the roots or muscles of the spine, in both healthy persons and individuals with strokes or spine disorders, is highlighted in several scientific studies thanks to its positive effects.
After magnetic stimulation, considerable changes were observed in neurophysiological and biomechanical actions and clinical results. Changes in spasticity were also observed and the dynamics of muscle movement were improved as well.
Improvement of muscle spasticity with Capenergy
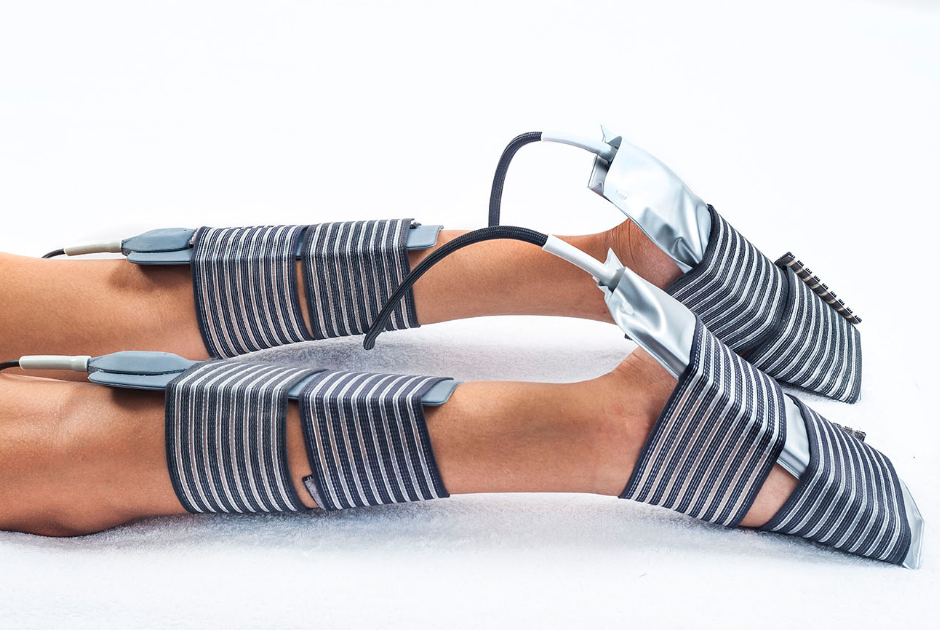
The application of radiofrequency with CAPENERGY effectively improves muscle spasticity. It has furthermore been proven that the personalized energy delivery, achieved by controlling both the power level and the amount of delivered energy, as well as the increase of the treatment surface, enable a better energy absorption which improves muscle mobility and increases muscle relaxation, thus contributing to a slow but steady recovery of the spastic muscle.
In patients under treatment, a reduction of the muscle spasticity is observed.
Furthermore, with lymphatic drainage after the treatment we can mobilize substances towards the thoracic conduct, leaving the muscle with very little waste metabolites.
One of the advantages of Capenergy’s technology in the treatment of muscle spasticity, are the automatic treatments. With these treatment, it is possible for the patient, still suffering from uncontrolled movements, to receive the effects of radiofrequency, working at low temperatures due to the natural insensitivity of this type of patients. Temperature can furthermore be controlled to avoid burns or any other risks for the patient.
It is without any doubt a pleasant and painless treatment for the patient suffering from muscle spasticity.

As mentioned before, electromedical therapies have a good reputation in the medical community for the treatment of this type of patients, especially with regards to the improvement of quality of life. In combination with the application of BOTOX, or botulinum toxin, radiofrequency can extend the period of time between one injection and the other. Botox can be useful in the treatment of spasticity as it weakens the infiltrated muscles, but the effect tends to disappear after 3 to 6 weeks.
It is possible for patients with muscular spasticity to generate a resistance to the BOTOX type of proteins, which reduces the effect and tends to give way to more invasive solutions. CAPENERGY’s technology can avoid this from happening, in combination with other techniques.
How to apply Capenergy radiofrequency in patients suffering from muscle spasticity
Capenergy’s proposed radiofrequency treatment, which can be adapted to each pathology, type of patient and treatment area, would be the following:
- Automatic treatment for 20/30 minutes, obtaining an initial localized vascularization stimulating the lower and upper limbs as a lymphatic drainage and or a specific neuronal treatment that covers the entire back area from the cervicals in the base of the neck to the sacrococcygeal area stimulating blood irrigation in general as well as its effects on muscular level.
- Manual application immediately after for 10/20 minutes with capacitive and resistive electrodes at the same time, in a specific area selected by the therapist.
- The treatment ends with 10 minutes of lymphatic drainage, placing the active plate on the treated limb and closing the circuit by placing the passive plate in proximal or distal mode, according to the desired effect.
Capenergy’s TecarEvolution is without any doubt a great high performance technological ally for physiotherapists and neurologists for the treatment of patients suffering from muscle spasticity.
Capenergy’s technology is a therapeutic alternative with long term results. It ‘s a biological, non-invasive treatment, contributory to other therapies and efficient for chronic pain and muscle relaxation in general, increasing the patient’s quality of life.
Would you like to know more about Capenergy’s radiofrequency and how it can help improve the lives of your patients suffering from muscle spasticity? Request a free demo.